Cervical Cancer: What You Need To Know About The Signs And Symptoms Of End-Stage Disease’ Cervical cancer is a serious and life-threatening illness, and the sooner it’s diagnosed and treated, the better the prognosis for survival. But what about those suffering from end-stage cervical cancer? What are the signs and symptoms of this terminal stage of the disease? Read on to learn more about what you need to know about cervical cancer in its final stages.
When it comes to cervical cancer, there are typically three stages – early, locally advanced, and end-stage. However, in order to understand the signs and symptoms of end-stage disease, it’s important to have a general understanding of the disease as a whole.
Cervical Cancer: What You Need To Know About The Signs And Symptoms Of End-Stage Disease
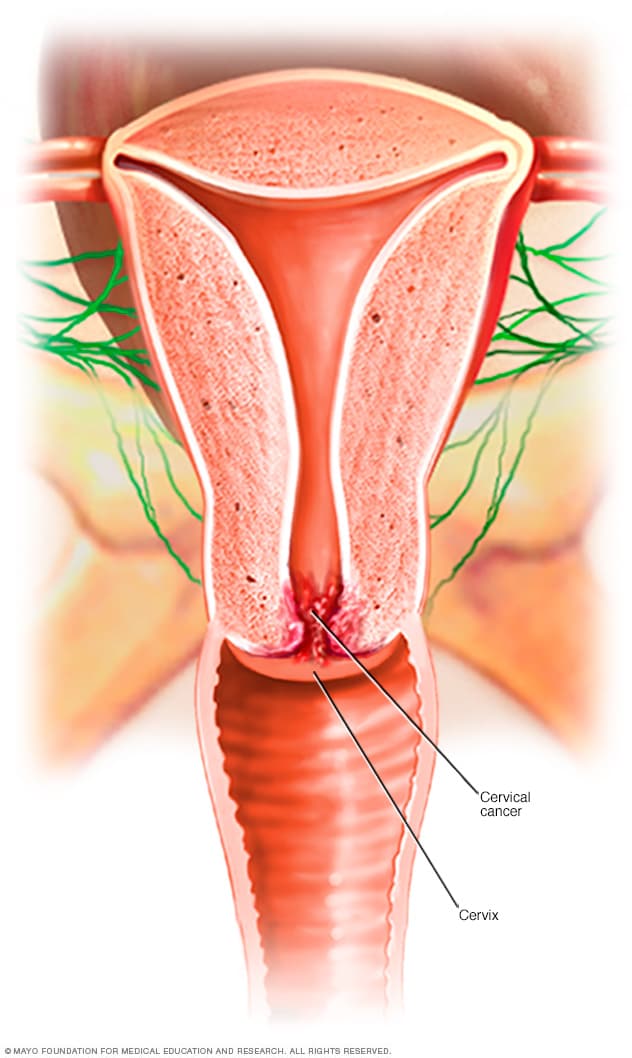
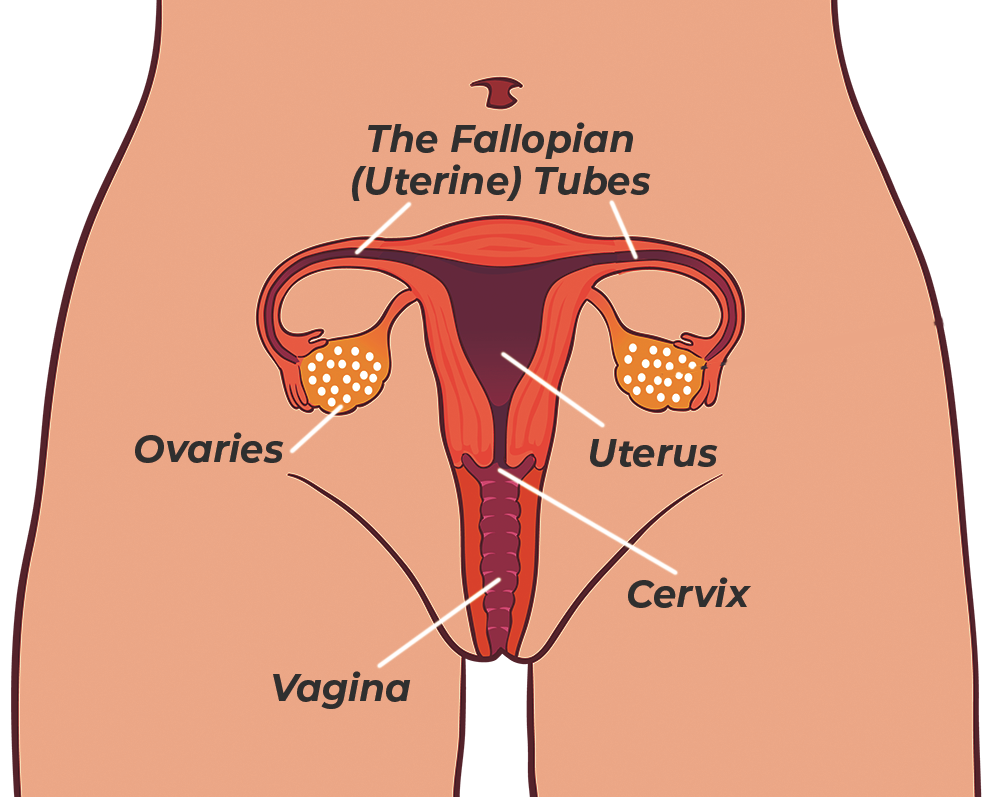
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the tissues of the cervix – the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. The vast majority of cervical cancers are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is a sexually transmitted infection. In fact, HPV is responsible for almost all cases of cervical cancer in women under the age of 35.
There are two main types of HPV: low-risk and high-risk. Low-risk HPV can cause genital warts, but it does not usually lead to cancer. High-risk HPV can cause abnormal cell changes on the cervix, which can eventually lead to cancer if left untreated.
Most women with HPV do not develop cervical cancer because their bodies are able to clear the virus naturally. However, some women develop persistent infections with high-risk HPV strains that can lead to precancerous lesions on the cervix. Precancerous lesions are abnormal cell growths that have not yet turned into cancer but have the potential to do so if left untreated.
Cervical cancer usually develops slowly over time, starting with precancerous lesions that progress early.
READ POST: 5 Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer – How To Catch It Early
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is most often caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can be passed from person to person through sexual contact. There are many different types of HPV, and some types can lead to cervical cancer while others do not. Other less common causes of cervical cancer include smoking, a weakened immune system, and exposure to certain chemicals.
Most cases of cervical cancer are caused by HPV. HPV is a group of viruses that are passed from person to person through sexual contact. There are many different types of HPV, and some types can lead to cervical cancer while others do not. The vast majority of people who have HPV will never develop cervical cancer.
Smoking cigarettes can also increase your risk for developing cervical cancer. Cigarette smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage the cells lining the cervix, making them more susceptible to mutations that can lead to cancer. If you smoke and have HPV, you are even more likely to develop cervical cancer than someone who just has HPV.
A weakened immune system also increases your risk for developing cervical cancer. People with HIV or AIDS are at an increased risk because their immune systems are unable to fight off infections as well as healthy people. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy can also weaken the immune system, which is why women undergoing treatment for other cancers may be at an increased risk for developing cervical cancer.
Finally, exposure to certain chemicals has been linked with an increased risk of developing
Stages of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a serious disease that can be deadly if left untreated. However, early detection and treatment can often lead to a full recovery. There are four main stages of cervical cancer, each with different symptoms and treatment options.
Stage I: In stage I, the cancer is confined to the cervix and has not spread to other parts of the body. The most common symptom of stage I cervical cancer is abnormal bleeding from the vagina, which may occur after sex or during menstrual periods. Other possible symptoms include pain during sex, unusual vaginal discharge, and pelvic pain. Treatment for stage I cervical cancer usually involves surgery to remove the cancerous tissue, followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy.
Stage II: In stage II, cancer has spread beyond the cervix but is still confined to the pelvic region. The most common symptom of stage II cervical cancer is abnormal bleeding from the vagina, which may occur after sex or during menstrual periods. Other possible symptoms include pain during sex, unusual vaginal discharge, and pelvic pain. Treatment for stage II cervical cancer usually involves surgery to remove the cancerous tissue, followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy.
Stage III: In stage III, cancer has spread beyond the pelvis and into the abdomen or lymph nodes in the neck or elsewhere in the body. The most common symptom of stage III cervical cancer is abnormal bleeding from the vagina, which may occur after sex or during menstrual periods. Other possible symptoms include pain
READ: 5 Healthy Foods You Should Keep In Your Fridge For Quicker Weight Loss
Risk Factors for Developing Cervical Cancer
There are a number of risk factors that can contribute to the development of cervical cancer. One of the most significant risk factors is Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection. HPV is a sexually transmitted virus that can cause changes in the cells of the cervix, which can lead to cancer. Other risk factors include:
-smoking
-family history of cervical cancer
-history of abnormal Pap smears
-weak immune system
-long-term use of oral contraceptives
If you have any of these risk factors, it is important to talk to your doctor about how to best reduce your risk of developing cervical cancer.
Signs and Symptoms of End-Stage Cervical Cancer
As the final stage of cervical cancer, the end-stage disease can present a number of different signs and symptoms. In some cases, cancer may not cause any symptoms at all. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include:
-Abnormal bleeding from the vagina
-Pain in the pelvis or lower back
-Problems urinating
-Loss of appetite and weight loss
-Fatigue and a general feeling of ill health
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor as soon as possible. End-stage cervical cancer is very difficult to treat and the earlier it is diagnosed, the better the chances of successful treatment.
Treatment Options for End-Stage Cervical Cancer
End-stage cervical cancer is a difficult diagnosis to receive, but there are treatment options available. While chemotherapy and radiation are the most common methods of treatment, there are also other options available for those who cannot or do not want to undergo traditional treatment. These include targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and clinical trials.
Targeted therapy is a newer form of cancer treatment that uses drugs or other substances to target specific cancer cells without damaging healthy cells. Immunotherapy helps the body’s immune system fight cancer by boosting it or by helping it work better. Clinical trials test new treatments in people to see if they are safe and effective before they become widely available.
No matter what treatment option you choose, it is important to have a support system in place. Family and friends can be great sources of support, but there are also many organizations and online communities dedicated to providing support for those with cervical cancer.
Coping with End-Stage Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a serious disease that can have a profound impact on a woman’s health. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of end-stage cervical cancer so that you can seek treatment early and improve your prognosis.
End-stage cervical cancer is typically characterized by the spread of the disease to other parts of the body, including the liver, lungs, and brain. This can lead to a host of serious symptoms, including pain, fatigue, weight loss, and problems with urination and bowel movements. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor immediately so that they can determine if you have end-stage cervical cancer.
Once diagnosed with end-stage cervical cancer, there are a number of treatment options available. These include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The type of treatment that is right for you will depend on the stage of the disease and your overall health. It is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
In addition to treatment, there are a number of things you can do at home to help cope with end-stage cervical cancer. These include staying active and eating a healthy diet. Exercise can help reduce fatigue and promote overall health. Eating a healthy diet can help improve your energy levels and maintain your strength during treatment. There are also many support groups available for women coping with cervical cancer. These groups can provide emotional support and
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is a serious disease, and it’s important to know the signs and symptoms of end-stage cervical cancer. If you have any concerns or symptoms that could be related to cervical cancer, talk with your doctor right away. Early diagnosis can lead to more successful treatments and better outcomes for those affected by this condition. Taking care of ourselves and staying informed are two essential steps in preventing the further spread of this type of cancer.
READ ALSO: Is There Any Side Effect To Eating Guava During Pregnancy?